At a Glance
- What the NIST AI RMF is and how it shapes responsible AI governance.
- Why AI risk management matters for compliance, security, and ethics.
- Core principles and functions (Govern, Map, Measure, Manage) that drive trustworthy AI.
- How organizations can implement NIST AI RMF to align with global regulations.
- How adopting the framework boosts credibility and stakeholder trust across industries.
Artificial intelligence holds immense potential to transform society, driving significant economic and social growth. However, alongside its benefits come various risks—ranging from short- to long-term, low-probability to high-impact, and systemic to localized challenges. These risks make AI a uniquely complex technology to implement effectively across organizations and society. The NIST AI RMF plays a vital role in guiding AI risk management, supporting the responsible use of AI systems. It emphasizes the need for human-centric design and social responsibility in AI development and deployment.
Organisations and their teams engaged in the design, development, and implementation of AI are encouraged by AI risk management to thoroughly evaluate the context and any possible advantages or disadvantages. In the end, this critical thinking regarding the risks of AI systems and how to handle them will promote credibility and increase public trust.
As directed by the National Artificial Initiative Act of 2020, the aim of NIST AI RMF is to provide resources to organizations for designing, developing, deploying, or using AI systems to help manage, in addition to addressing the many hazards that come with AI, this framework seeks to promote its responsible and trustworthy development and application. It is meant to be voluntary, rights-preserving, flexible across all industries, and independent of specific use cases.
Its adaptability makes it possible for businesses of all sizes, across all sectors of the economy, and across society to use its methods. This framework will help increase the trustworthiness of AI systems that help in design, deployment, and development. The NIST AI RMF is to be practical, which helps to adapt to AI landscape as AI technologies. Wherein risk is a composite measure of events probability occurring and the consequences of the corresponding event.
Where risk management addresses the negative impact of this framework to minimize the negative impacts that can help to understand AI model uncertainty. The NIST AI RMF effectively addresses the new risk wherein it is not easy to foresee. Some of the related risks are
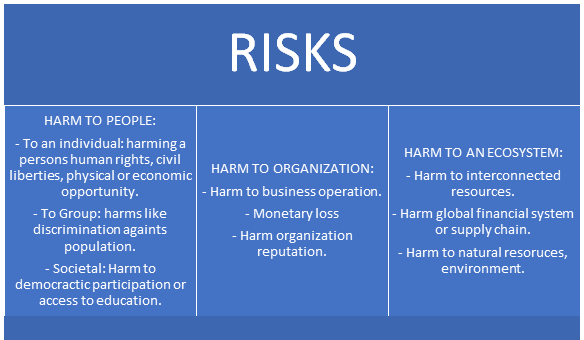
To address these risks, NIST AI RMF was created on October 30, 2024, AI executive order with the objectives as follows:
- To enable organizations to identify potential threats before they create an impact.
- To establish actionable standards for managing AI risks.
- To build ethical, secure AI to establish public trust.
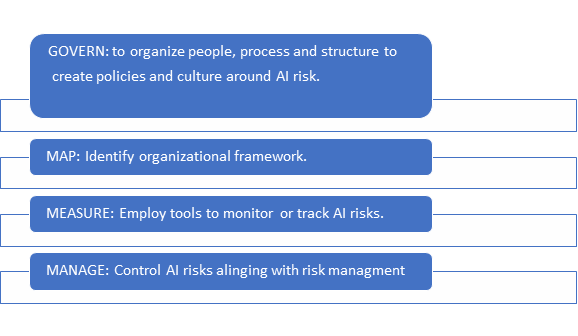
The NIST framework provides a socio technical perspective helping business to align with its values with trust worthy AI system wherein it focuses on Core functions like:
Why do we Need AI Risk Management:
- The use of AI in organizations have expanded the risks associated with AI.
- With the increase of regulations on AI the AI models are better to be explained and also ensure privacy standards.
- The implications of AI technology into business model that can help to increase transparency.
HOW CAN ONE ORGANIZATION GET EFEFCTIVELY STARTED WITH NIST AI RMF:
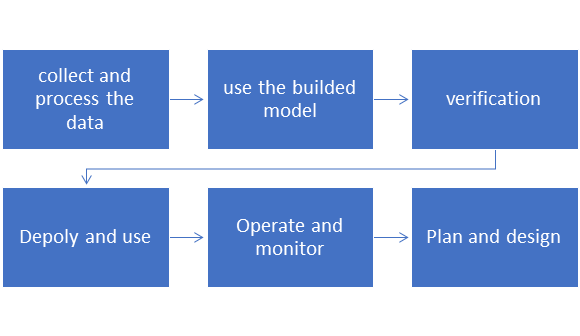
The above flow chart shows that organizations should assess their current AI capabilities and strategy and how it intersects with broader ERM efforts. Because of the framework’s flexibility, businesses can modify their AI procedures to adhere to applicable laws, rules, and industry norms, which might range greatly throughout industries. An organisation can utilise the framework’s advice to evaluate risks, ascertain their risk tolerance, rank risks, and incorporate these AI-related risk management principles into their operations when they have developed a fundamental understanding of AI risk.
To guarantee that their AI systems continue to be reliable, organisations should regularly review and improve how they apply the NIST framework’s fundamental features and risk management techniques as their AI capabilities advance. Some of the illustrative activities related to NIST AI RMF core functions are:
1. Baseline activities to establish trustworthy AI:
- GOVERN: Combine risk management for AI with current organisational structures: Provide mechanisms to guarantee that AI risk management aligns with the organization’s guiding principles, established guidelines, and overarching strategic objectives.
- Give AI systems clear responsibilities: Make and keep records that specify who is responsible for certain facets of AI systems and the procedures that go along with them.
- MAP: Access AI capabilities and determine organizational risk tolerances.
- MEASURE: Define AI risk and its control measures thereby to monitor AI system and productions.
- MANAGE: Document the AI risk and decide which to prioritize to align it with organizational strategy.
2. Activities to Enhance AI trustworthiness:
- GOVERN: Establish mechanism for the teams to deploy AI systems to incorporate feedbacks from stakeholders into their system updates.
- MAP: Map risks related to data supply and AI systems. Create processes to understand the drift in model over period.
- MEASURE: Monitor existing AI risks and also form reporting and feedback mechanism to measure AI trustworthy characteristics.
- MANAGE: Form robust, issue management and communication processes also monitor third party AI resources.
FURTHER NIST CHARCTERITICS OF TRUSTWORTHY AI ARE:
1. Valid and Reliable:
Validation is the “confirmation through the provisions of objective evidence, that the requirements for a specific intended use or application have been fulfilled.” AI systems that are unreliable or have poor data management increase negative AI risks and reduce credibility.
Reliability means “ability of an item to perform as required, without failure, for a given time interval, under given conditions”3 This function helps for overall correctness of AI system over time period.
This both functions help AI system to access and monitor the functioning of the system that can help to access the failure causing harms, the AI risk management aims to reduce negative impacts.
2. Accountable and Transparent:
Measures to enhance transparency and accountability help to understand the impact of risk and appoint safeguard measures. For transparency and accountability, it is essential to keep accurate records of the training data used by an AI system linking it with data subsets, ensuring protection of copyrights of the training data. As documentation and tools for AI transparency continue to grow, AI developers should work with those implementing these systems to thoroughly test various technologies. This cooperative testing guarantees that AI systems are utilised exactly as planned and that the necessary stakeholders can comprehend how they operate.
- Safe:
Safe operation of AI systems is improved through:
- Responsible design, development, and deployment practices;
- Clear information to deployers on responsible use of the system;
- Responsible decision-making by deployers and end users; and
- Explanations and documentation of risks based on empirical evidence of incidents.
3. Secure and Resilient:
AI systems are said to be resilient if they can continue to function and safely degrade when needed in the face of unforeseen circumstances, changes in the environment, or modifications in their intended usage. However, resilience is only one aspect of security. Security is taking proactive steps to stop, defend against, respond to, and recover from assaults, whereas resilience is about overcoming unfavourable circumstances.
Data poisoning, intellectual property theft, and adversarial instances are common security issues. Secure AI systems use safeguards to preserve availability, confidentiality, and integrity. Here, NIST guidelines are pertinent. Resilience is essentially a part of security, which is primarily concerned with preserving AI systems’ functionality and integrity against any attacks, even malevolent ones.
4. Explainable and Interpretable:
Privacy enhancing technologies can support AI system to ensure values like fairness data protection. This system also helps in identify new risks related to privacy, it helps to inference to identify individuals’ private information about individuals.
5. Fair with Harmful Bias Managed:
Bias in AI is more than just having uneven data. According to NIST, there are three primary kinds that can appear without deliberate bias: systemic, computational/statistical, and human-cognitive. Throughout the AI lifespan, organisational procedures or cultural norms might give rise to systemic bias. Errors in algorithms or non-representative data samples are the sources of computational and statistical bias.
The way people view and understand AI data or the system’s intent is known as human-cognitive bias. Although bias isn’t always bad, AI has the potential to severely magnify and accelerate detrimental biases, which can have an effect on people, communities, and society as a whole. Therefore, managing bias is important to ensure fairness and privacy.
Organizations looking to strengthen their risk management approach can explore this source to align with frameworks like the NIST AI RMF 1.0.
The Effectiveness OF AI RMF:
- Enhance process of governing, mapping, measuring and managing AI risk
- Improve awareness on AI risks.
- Explain process for go or no-go systems.
- Establish policies for organizations to accountability efforts related to AI system.
- Greater knowledge on downstream risks
- Strengthen engagement between interested parties.
- To provide common language to manage AI risks.
- Be outcome-focused and non-perspective.
CONCLUSION:
Hence the NIST AI RMF is a path to develop AI and understand the AI risk thereby related regulation. Adopting this system can help organizations ethical, secure compliance with global regulations. The system develops a path to develop AI to tackle challenges on transparency, data governance and develop a trust worthy AI across border that can help in alignment with business strategy and operations this can ensure fairness, privacy and ethics for the data used for AI system.
Adaptive AI works on the same values to ensure AI risk management and implement NIST AI RMF more easily and effectively, which helps the organizations work on risk and monitor it properly so that they can develop a safe environment ensuring compliance with the regulations.
FAQs
1: What is the NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF)?
The NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF) is a comprehensive guideline developed by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology to help organizations identify, assess, manage, and mitigate risks associated with artificial intelligence systems. It promotes the creation of trustworthy, transparent, and secure AI by focusing on four key functions: Govern, Map, Measure, and Manage.
2: Why is AI risk management important for organizations?
AI risk management is essential because AI systems can unintentionally cause harm—from data bias and privacy violations to regulatory non-compliance and reputational damage. By implementing structured frameworks like the NIST AI RMF, organizations can reduce operational and ethical risks, maintain regulatory compliance, and enhance public trust in their AI systems.
3: How can organizations get started with the NIST AI RMF?
To effectively implement the NIST AI RMF, organizations should start by assessing their current AI maturity, identifying potential risk areas, and mapping these risks to existing enterprise risk management (ERM) processes. The next step is to align their governance structure, data management, and model documentation with the NIST AI RMF’s core functions—ensuring continuous monitoring, improvement, and accountability throughout the AI lifecycle.
4: What are the core principles of trustworthy AI defined by NIST?
NIST defines a trustworthy AI system as one that is:
- Valid and Reliable
- Accountable and Transparent
- Safe, Secure, and Resilient
- Explainable and Interpretable
- Fair with Harmful Bias Managed
These principles ensure that AI systems are not only technically sound but also socially responsible and ethically aligned.
5: How does Adeptiv AI help organizations implement the NIST AI RMF?
Adeptiv AI enables organizations to operationalize the NIST AI RMF through automation and governance tools that simplify compliance, documentation, and monitoring. The platform helps map AI risks, measure trustworthiness, and manage regulatory requirements — ensuring that teams can build and deploy responsible AI systems that align with both NIST standards and emerging global AI regulations.



